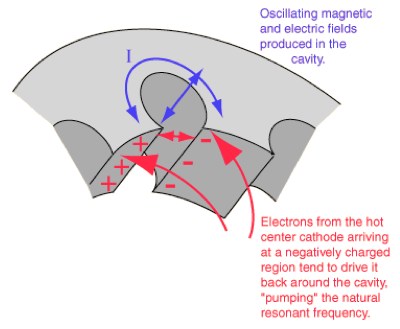
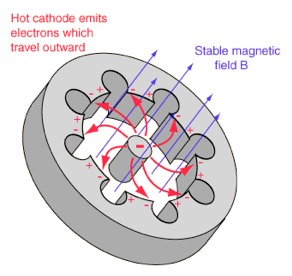
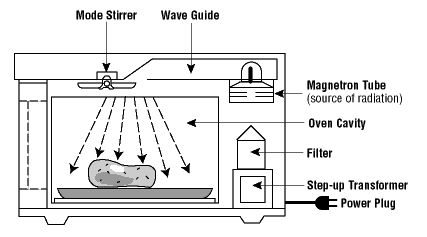
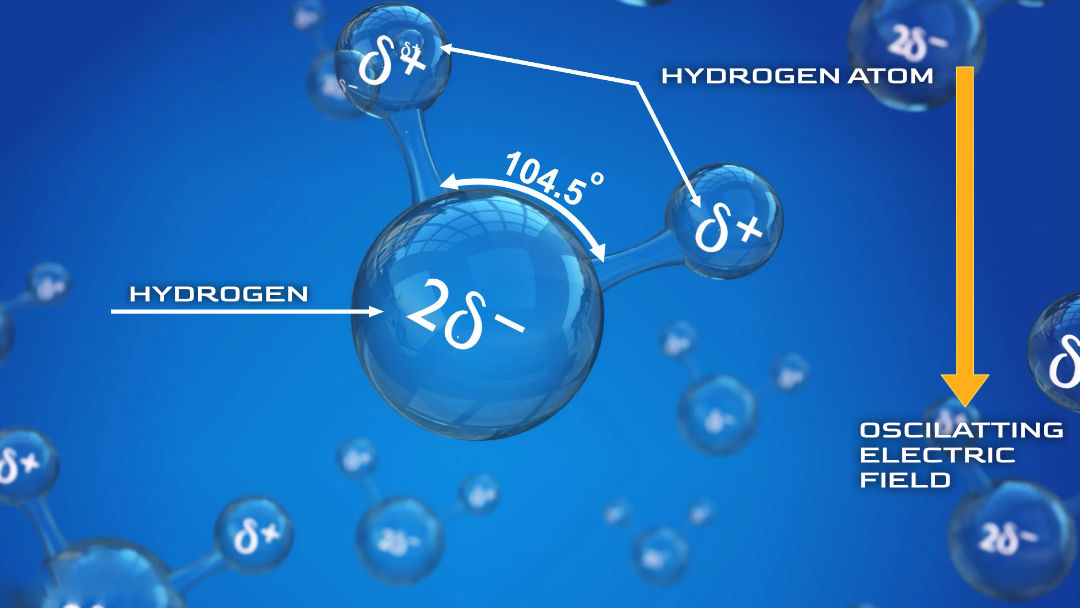
Safe and Sound - Environmental Factors - Microwaves - blog 15 - Blog - Safe and Sound - element14 Community
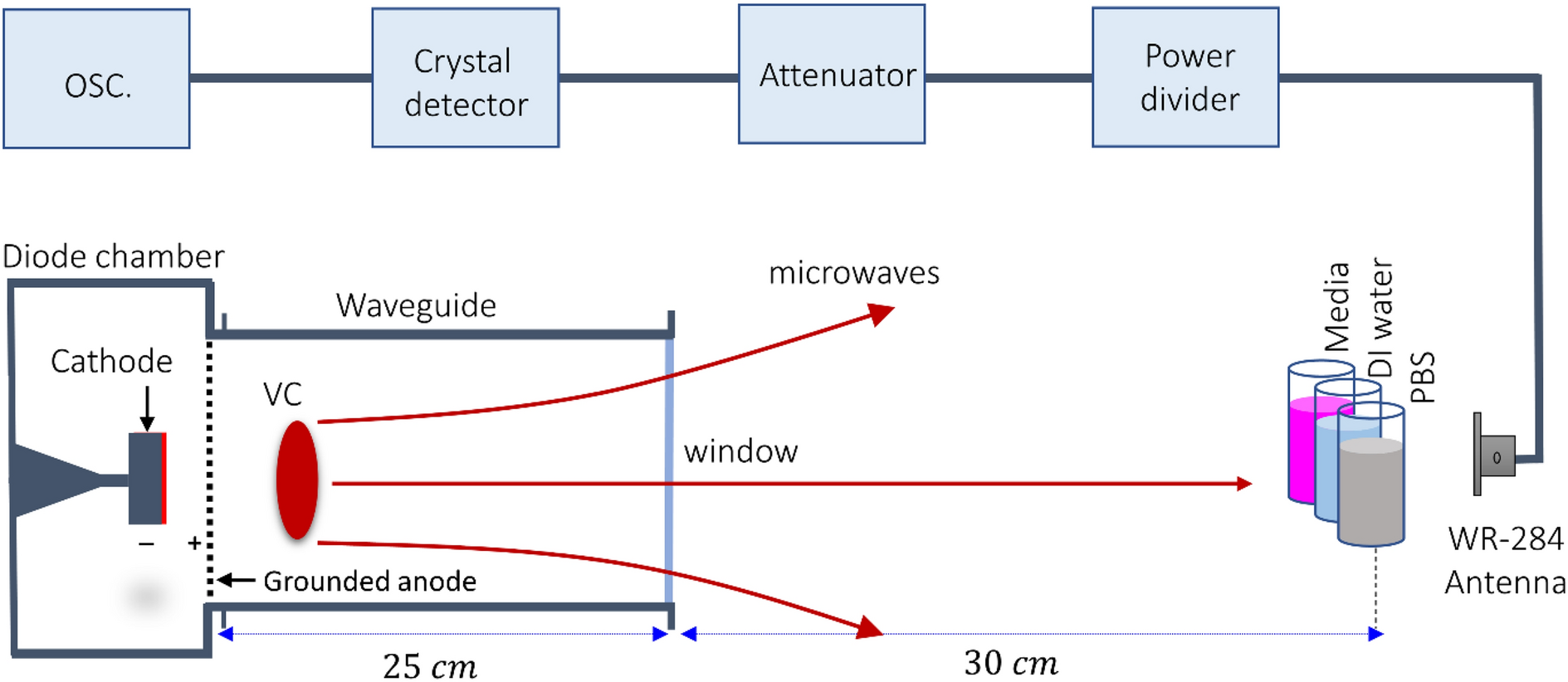
Pulsed 3.5 GHz high power microwaves irradiation on physiological solution and their biological evaluation on human cell lines | Scientific Reports

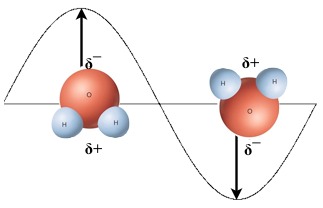
An EM wave consists of 2 components: electric field and magnetic field,... | Download Scientific Diagram

A) The electric field norm distribution inside microwave P = 1200 W... | Download Scientific Diagram
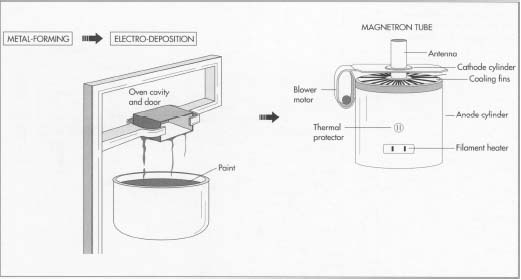
How microwave oven is made - manufacture, making, used, parts, components, structure, product, Design
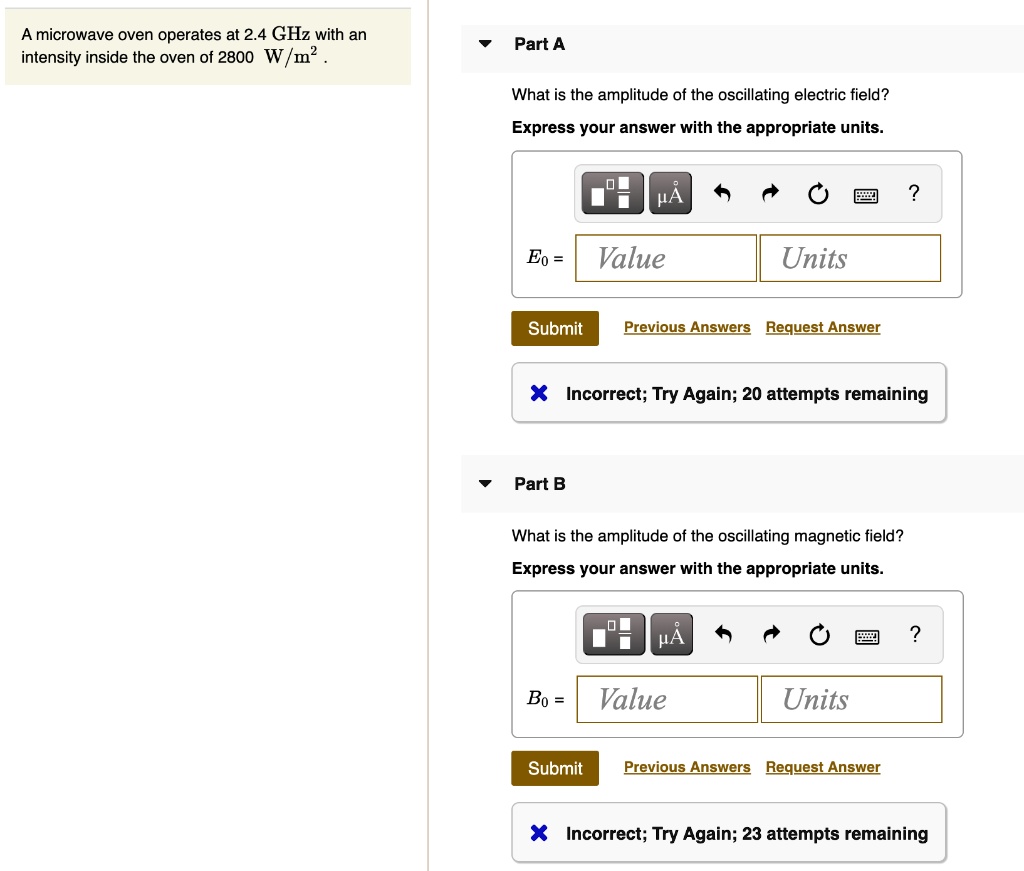
SOLVED: A microwave oven operates at 2.4 GHz with an intensity inside the oven of 2800 W /m? Part A What is the amplitude of the oscillating electric field? Express your answer
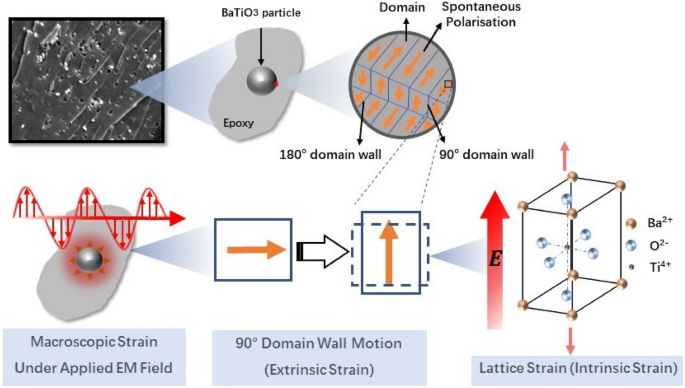
Electromagnetic field controlled domain wall displacement for induced strain tailoring in BaTiO3-epoxy nanocomposite | Scientific Reports